GenDBWiki/WebDocumentation/DialogWindows/SNP-Detector: Difference between revisions
imported>SebastianKonietzny No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
SNP-Detector detects and lists Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in genomic data. | '''SNP-Detector detects and lists Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in genomic data.''' | ||
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (abbreviated SNPs,pronounced "snips") are a phenomenon related to homologous sequences. They describe little (regularly only one base is affected) differences between strongly related, homologous sequences. SNPs may fall within coding sequences (CDS) of genes or between genes (intergenic regions). SNPs are due to single nucleotide mutations (substitution, deletion or insertion of a single nucleotide) which may happen independently on the single sequences. Normally, for a variation to be considered a SNP, it must occur in at least 1% of the population. SNP-Detector, though, is not be seen in the context of this statistical approach, but reports all single nucleotide variations between homologous sequences (CDS-regions or intergenic regions) of two contigs belonging to strongly related organisms. | ''Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms'' (abbreviated SNPs,pronounced "snips") are a phenomenon related to homologous sequences. They describe little (regularly only one base is affected) differences between strongly related, homologous sequences. SNPs may fall within coding sequences (CDS) of genes or between genes (intergenic regions). SNPs are due to single nucleotide mutations (substitution, deletion or insertion of a single nucleotide) which may happen independently on the single sequences. Normally, for a variation to be considered a SNP, it must occur in at least 1% of the population. SNP-Detector, though, is not to be seen in the context of this statistical approach, but reports all single nucleotide variations between homologous sequences (CDS-regions or intergenic regions) of two contigs belonging to strongly related organisms. | ||
SNPs are important features of a genomic sequence. Their distributions are normally characteristic for a specific strain. SNPs are often used for rapid classification of an organism. Since SNPs in CDS sequences may change codons they can also differ the function of genes and therefore be responsible for altered phenotypical characteristics of mutants. A convenient method for detecting SNPs is restriction fragment length polymorphism (SNP-RFLP). | SNPs are important features of a genomic sequence. Their distributions are normally characteristic for a specific strain. SNPs are often used for rapid classification of an organism. Since SNPs in CDS sequences may change codons they can also differ the function of genes and therefore be responsible for altered phenotypical characteristics of mutants. A convenient method for detecting SNPs is restriction fragment length polymorphism (SNP-RFLP). | ||
Starting SNP-Detector and general remarks | <span id="StartingSNPDetection"></span> | ||
== Starting SNP-Detector and general remarks == | |||
As described above SNP-Detector can be used to list all single nucleotide variations between two strongly related contigs. This is achieved by analyzing blast-results computed for the sequences (CDS or intergenic regions) of one contig (named "source" in the following) against the corresponding sequences of another (strongly related) contig (named "target" in the following). SNP-Detector therefore relies on the results of BLAST-tools from the projects database which already have to be run for the contigs in a former stage as a precondition. | |||
---- | |||
To open the SNP-Detector configuration page you have to select the option "SNP Detection" from the category "Edit" in the main menue. A new window will be opened and you will see the configuration page. | To open the SNP-Detector configuration page you have to select the option "SNP Detection" from the category "Edit" in the main menue. A new window will be opened and you will see the configuration page. | ||
---- | |||
'''''Notice, that SNP-Detector may be run for both types of sequences, CDS and intergenic regions, independently!''''' | |||
<span id="SNPConfiguration"></span> | |||
== Configuring SNP-Detector == | |||
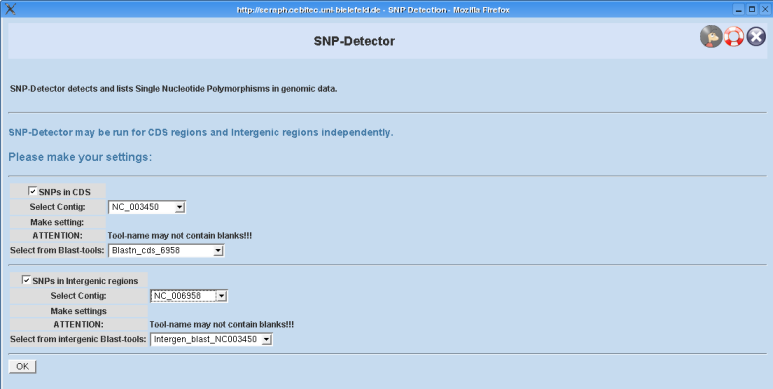
[[ | [[File:SNP-Detector-Config.png|Screenshot of the SNP Detector configuration dialog.]] | ||
---- | |||
Options: | |||
Mode selection: | '''Mode selection:''' | ||
On the configuration page the user can choose whether he wants SNP-Detector to be run for CDS regions or intergenic regions only, or for both. You simply have to check out the corresponding boxes named "CDS | On the configuration page the user can choose whether he wants SNP-Detector to be run for CDS regions or intergenic regions only, or for both. You simply have to check out the corresponding boxes named "SNPs in CDS" or "SNPs in intergenic regions", respectively. | ||
The following options are similar in both modes and will therefore be explained only once! | '''The following options are similar in both modes and will therefore be explained only once!''' | ||
Selecting a contig: | '''Selecting a contig:''' | ||
Depending on what mode you have selected you can now select a contig object from the projects database. This contig must be regarded as the "source" contig (see | Depending on what mode you have selected you can now select a contig object from the projects database. This contig must be regarded as the "source" contig (concerning the term "source contig" in this context see also section [[#StartingSNPDetection|general remarks]]), that means, that the BLAST tool you will select in a following step must have been executed on this contig! | ||
Selecting a BLAST tool: | '''Selecting a BLAST tool:''' | ||
Here you can select a suitable tool for your purpose. That means, that the tool's predefined database must be related to the "target" contig (see also section [[#StartingSNPDetection|general remarks]]), since its results where computed for the "source" contig and therefore the combination makes sense. | |||
When you are ready you can submit the page! | |||
EXAMPLE | ---- | ||
The BLAST-tool "Blast2n_vs_NC_YYYY" with its predefined database "NC_YYYY.cds" was run on contig NC_XXXX! In this case NC_XXXX is the "source" contig, whereas "NC_YYYY" is said to be the "target" contig. Therefore you would select the tool | EXAMPLE FOR CORRECT USE: | ||
The BLAST-tool "Blast2n_vs_NC_YYYY" with its predefined database "NC_YYYY.cds" was run on contig NC_XXXX! | |||
In this case NC_XXXX is the "source" contig, whereas "NC_YYYY" is said to be the "target" contig. Therefore you would select the tool's name from the popup-menue and choose the contig "NC_XXXX" from the popup-menue displaying all contigs in the project! | |||
---- | |||
NOTE | '''NOTE THAT THE NAME OF THE SELECTED BLAST-TOOL MUST NOT CONTAIN BLANKS!''' | ||
'''''This is due to the fact, that the processing is made on the cluster and this is a restriction which momentarily has to be made. You ought to keep this in mind, when you create your tools.''''' | |||
'''''The intergenic regions are not region objects in GENDB as for example CDS regions are. They are only computed for the BLAST step and will not be stored in the project's database! That is why you have to use a specific BLAST-tool belonging to the class GENDB::Intergenic_Blast!''''' | |||
SNP-Detector is running | == SNP-Detector is running == | ||
When you have submitted the configuration and the tool's checks does not detect any problems you will be informed that your job is in process. Please keep this information page open, since it will show the results later on. Since SNP-Detector checks all the sequences of the contig the computation may last a period of time. | When you have submitted the configuration and the tool's checks does not detect any problems you will be informed that your job is in process. Please keep this information page open, since it will show the results later on. Since SNP-Detector checks all the sequences of the contig the computation may last a period of time. | ||
SNP-Detector | == SNP-Detector overview page == | ||
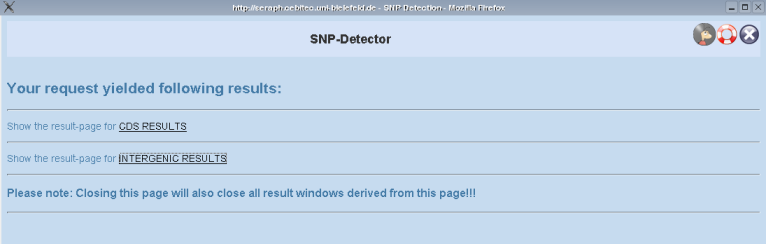
When SNP-Detector performed the computation you will be redirected to an overview page containing links to your results for CDS regions or intergenic regions (depending on your settings in the former stages). | When SNP-Detector performed the computation you will be redirected to an overview page containing links to your results for CDS regions or intergenic regions (depending on your settings in the former stages). | ||
Now, go on by clicking on of the links to your results! | |||
[[File:SNP-Detector-Results.png|Screenshot of the SNP Detector result overview.]] | |||
---- | |||
'''''PLEASE NOTE, that you should not close this page unless you want to discard all your results. As long as the overview page is open and your session does not expire your results remain accessible from that overview page.''''' | |||
Result | == Result pages == | ||
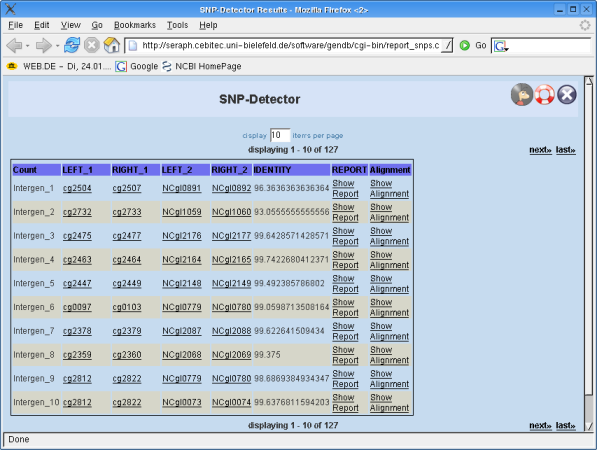
The result page shows the single results for all CDS regions or intergenic regions. The representation of the results differs for CDS regions and intergenic regions. See the appropriate section in this manual to get to know what the entries (single rows) in your result lists mean! To distinguish between "source" (1) and "target" contig (2) numbers were introduced that are appended on the column names as suffixes. Their meaning can be regarded as distinguishing between features related to "region 1" ("source") or "region 2" ("target"), respectively. | The result page shows the single results for all CDS regions or intergenic regions. The representation of the results differs for CDS regions and intergenic regions. See the appropriate section in this manual to get to know what the entries (single rows) in your result lists mean! To distinguish between "source" (1) and "target" contig (2) numbers were introduced that are appended on the column names as suffixes. Their meaning can be regarded as distinguishing between features related to "region 1" ("source") or "region 2" ("target"), respectively. | ||
CDS Regions: | ---- | ||
'''CDS Regions:''' | |||
You will see the names of the two CDS regions (on "source" and "target" contig) that are most likely to be homologous as calculated from the available BLAST results. These names represent links that will direct you to the corresponding objects in GENDB. You also see the PERCENT IDENTITY of the hit and the LENGHT of the hit. | You will see the names of the two CDS regions (on "source" and "target" contig) that are most likely to be homologous as calculated from the available BLAST results. These names represent links that will direct you to the corresponding objects in GENDB. You also see the PERCENT IDENTITY of the hit and the LENGHT of the hit. | ||
If you actually want to see an overview of the detected SNPs you must click on the link named "Show Report". The link "Show Alignment" will direct you to a new window where you can see the alingment of the two sequences. | If you actually want to see an overview of the detected SNPs you must click on the link named "Show Report". The link "Show Alignment" will direct you to a new window where you can see the alingment of the two sequences. | ||
----- | |||
Intergenic regions: | '''Intergenic regions:''' | ||
First you see a name for the intergenic region. This name is arbitrary and merely represents a | First you see a name for the intergenic region. This name is arbitrary and merely represents a counter for the regions. ''The intergenic regions are not region objects in GENDB as for example CDS regions are. They are only computed for the BLAST step and will not be stored in the project's database! That is why you have to use a specific BLAST-tool belonging to the class GENDB::Intergenic_Blast!'' | ||
You will see the names of the determined left and right flanking CDS regions (on "source" and "target" contig) for the intergenic regions that are most likely to be homologous as calculated from the available BLAST results. These names represent links that will direct you to the corresponding objects in GENDB. You also see the PERCENT IDENTITY of the hit and the LENGHT of the hit. | You will see the names of the determined left and right flanking CDS regions (on "source" and "target" contig) for the intergenic regions that are most likely to be homologous as calculated from the available BLAST results. These names represent links that will direct you to the corresponding objects in GENDB. You also see the PERCENT IDENTITY of the hit and the LENGHT of the hit. | ||
If you actually want to see an overview of the detected SNPs you must click on the link named "Show Report". The link "Show Alignment" will direct you to a new window where you can see the alingment of the two sequences. | If you actually want to see an overview of the detected SNPs you must click on the link named "Show Report". The link "Show Alignment" will direct you to a new window where you can see the alingment of the two sequences. | ||
---- | |||
[[File:SNP-Detector-List.png|Screenshot of the SNP Detector result list.]] | |||
---- | |||
It's possible to navigate through the result list. Closing the result page including the result list is no problem, since you can revisit the page from the overview page! | It's possible to navigate through the result list. Closing the result page including the result list is no problem, since you can revisit the page from the overview page! | ||
| Line 71: | Line 87: | ||
Since SNP-Detector stores its intermediate results in files you will get an information message that these files are deleted. This is normal! | Since SNP-Detector stores its intermediate results in files you will get an information message that these files are deleted. This is normal! | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[Category:Homepage]] | [[Category:Homepage]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:09, 30 November 2011
SNP-Detector detects and lists Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in genomic data.
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (abbreviated SNPs,pronounced "snips") are a phenomenon related to homologous sequences. They describe little (regularly only one base is affected) differences between strongly related, homologous sequences. SNPs may fall within coding sequences (CDS) of genes or between genes (intergenic regions). SNPs are due to single nucleotide mutations (substitution, deletion or insertion of a single nucleotide) which may happen independently on the single sequences. Normally, for a variation to be considered a SNP, it must occur in at least 1% of the population. SNP-Detector, though, is not to be seen in the context of this statistical approach, but reports all single nucleotide variations between homologous sequences (CDS-regions or intergenic regions) of two contigs belonging to strongly related organisms.
SNPs are important features of a genomic sequence. Their distributions are normally characteristic for a specific strain. SNPs are often used for rapid classification of an organism. Since SNPs in CDS sequences may change codons they can also differ the function of genes and therefore be responsible for altered phenotypical characteristics of mutants. A convenient method for detecting SNPs is restriction fragment length polymorphism (SNP-RFLP).
Starting SNP-Detector and general remarks
As described above SNP-Detector can be used to list all single nucleotide variations between two strongly related contigs. This is achieved by analyzing blast-results computed for the sequences (CDS or intergenic regions) of one contig (named "source" in the following) against the corresponding sequences of another (strongly related) contig (named "target" in the following). SNP-Detector therefore relies on the results of BLAST-tools from the projects database which already have to be run for the contigs in a former stage as a precondition.
To open the SNP-Detector configuration page you have to select the option "SNP Detection" from the category "Edit" in the main menue. A new window will be opened and you will see the configuration page.
Notice, that SNP-Detector may be run for both types of sequences, CDS and intergenic regions, independently!
Configuring SNP-Detector
Options:
Mode selection: On the configuration page the user can choose whether he wants SNP-Detector to be run for CDS regions or intergenic regions only, or for both. You simply have to check out the corresponding boxes named "SNPs in CDS" or "SNPs in intergenic regions", respectively.
The following options are similar in both modes and will therefore be explained only once!
Selecting a contig: Depending on what mode you have selected you can now select a contig object from the projects database. This contig must be regarded as the "source" contig (concerning the term "source contig" in this context see also section general remarks), that means, that the BLAST tool you will select in a following step must have been executed on this contig!
Selecting a BLAST tool:
Here you can select a suitable tool for your purpose. That means, that the tool's predefined database must be related to the "target" contig (see also section general remarks), since its results where computed for the "source" contig and therefore the combination makes sense.
When you are ready you can submit the page!
EXAMPLE FOR CORRECT USE:
The BLAST-tool "Blast2n_vs_NC_YYYY" with its predefined database "NC_YYYY.cds" was run on contig NC_XXXX! In this case NC_XXXX is the "source" contig, whereas "NC_YYYY" is said to be the "target" contig. Therefore you would select the tool's name from the popup-menue and choose the contig "NC_XXXX" from the popup-menue displaying all contigs in the project!
NOTE THAT THE NAME OF THE SELECTED BLAST-TOOL MUST NOT CONTAIN BLANKS! This is due to the fact, that the processing is made on the cluster and this is a restriction which momentarily has to be made. You ought to keep this in mind, when you create your tools.
The intergenic regions are not region objects in GENDB as for example CDS regions are. They are only computed for the BLAST step and will not be stored in the project's database! That is why you have to use a specific BLAST-tool belonging to the class GENDB::Intergenic_Blast!
SNP-Detector is running
When you have submitted the configuration and the tool's checks does not detect any problems you will be informed that your job is in process. Please keep this information page open, since it will show the results later on. Since SNP-Detector checks all the sequences of the contig the computation may last a period of time.
SNP-Detector overview page
When SNP-Detector performed the computation you will be redirected to an overview page containing links to your results for CDS regions or intergenic regions (depending on your settings in the former stages).
Now, go on by clicking on of the links to your results!
PLEASE NOTE, that you should not close this page unless you want to discard all your results. As long as the overview page is open and your session does not expire your results remain accessible from that overview page.
Result pages
The result page shows the single results for all CDS regions or intergenic regions. The representation of the results differs for CDS regions and intergenic regions. See the appropriate section in this manual to get to know what the entries (single rows) in your result lists mean! To distinguish between "source" (1) and "target" contig (2) numbers were introduced that are appended on the column names as suffixes. Their meaning can be regarded as distinguishing between features related to "region 1" ("source") or "region 2" ("target"), respectively.
CDS Regions: You will see the names of the two CDS regions (on "source" and "target" contig) that are most likely to be homologous as calculated from the available BLAST results. These names represent links that will direct you to the corresponding objects in GENDB. You also see the PERCENT IDENTITY of the hit and the LENGHT of the hit. If you actually want to see an overview of the detected SNPs you must click on the link named "Show Report". The link "Show Alignment" will direct you to a new window where you can see the alingment of the two sequences.
Intergenic regions: First you see a name for the intergenic region. This name is arbitrary and merely represents a counter for the regions. The intergenic regions are not region objects in GENDB as for example CDS regions are. They are only computed for the BLAST step and will not be stored in the project's database! That is why you have to use a specific BLAST-tool belonging to the class GENDB::Intergenic_Blast!
You will see the names of the determined left and right flanking CDS regions (on "source" and "target" contig) for the intergenic regions that are most likely to be homologous as calculated from the available BLAST results. These names represent links that will direct you to the corresponding objects in GENDB. You also see the PERCENT IDENTITY of the hit and the LENGHT of the hit. If you actually want to see an overview of the detected SNPs you must click on the link named "Show Report". The link "Show Alignment" will direct you to a new window where you can see the alingment of the two sequences.
It's possible to navigate through the result list. Closing the result page including the result list is no problem, since you can revisit the page from the overview page!
Closing the overview page: Since SNP-Detector stores its intermediate results in files you will get an information message that these files are deleted. This is normal!