MeltDBWiki/RoundingMZ: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>HeikoNeuweger No edit summary |
imported>HeikoNeuweger No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* Several mass spectral databases used for the identification of metabolites in GC/MS measurements (EI) contain mass spectra in nominal m/z notation whereas MS instruments are able to obtain higher resolution. | * Several mass spectral databases used for the identification of metabolites in GC/MS measurements (EI) contain mass spectra in nominal m/z notation whereas MS instruments are able to obtain higher resolution. | ||
* The mass spectral lookup using e.g. the ''dot-product' of the query and database spectra is | * The mass spectral lookup using e.g. the ''dot-product'' of the query and database spectra is inapropriate if high resolution spectra are compared to spectra with nominal m/z entries. One possibility is to transform the high resolution spectra to integral m/z values. Alternatively, adapted scoring methods can be applied. | ||
* High resolution mass spectra can be compared to nominal m/z spectra by ''rounding'' the measured m/z values to integral values. | * High resolution mass spectra can be compared to nominal m/z spectra by ''rounding'' the measured m/z values to integral values. | ||
* It is questionable if ''rounding'' at 0.5 is the best option. | * It is questionable if ''rounding'' at 0.5 is the best option. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Image:MeltDBWiki$$RoundingMZ$histmz.png]] | [[Image:MeltDBWiki$$RoundingMZ$histmz.png]] | ||
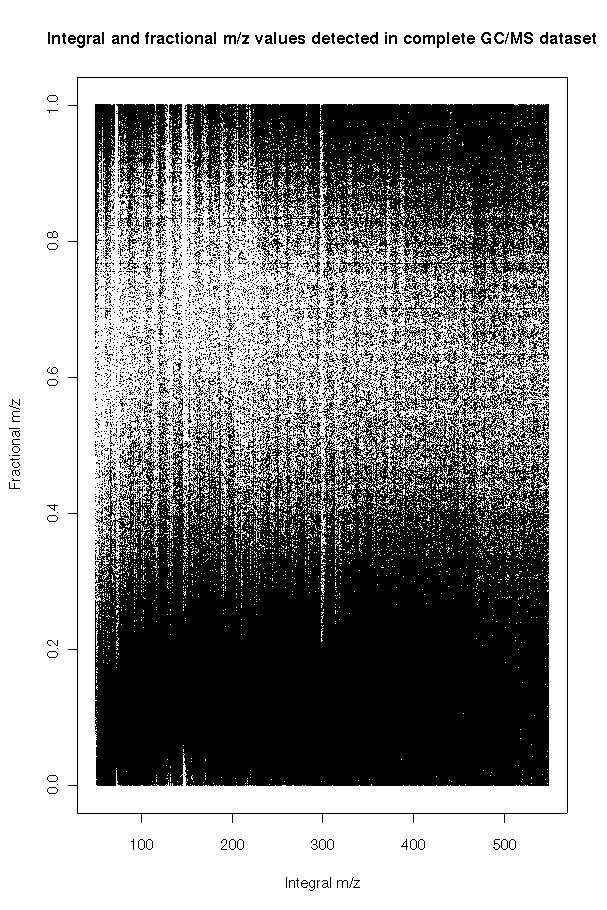
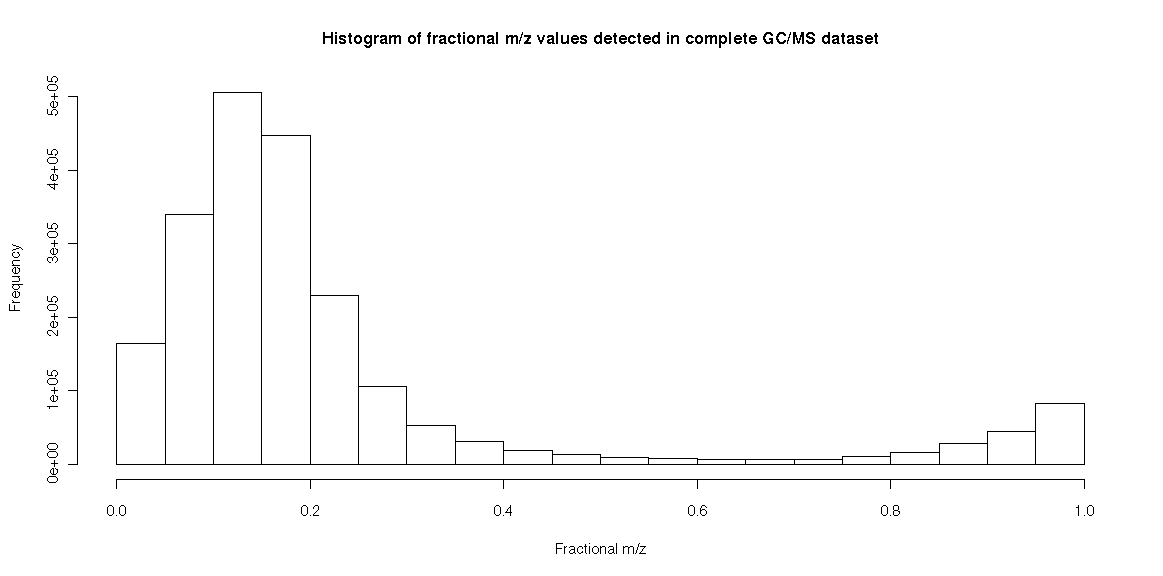
* For all | * For all m/z values detected by a MS instrument (EI, Ion Trap) for a complete chromatogram, the distribution of the values is comparable to that of the KEGG compounds. | ||
* Again, in the fractional interval 0.7 to 0.75 only 0.3% of the m/z values are detected. | * Again, in the fractional interval 0.7 to 0.75 only 0.3% of the m/z values are detected. | ||
Revision as of 21:12, 10 April 2008
Round m/z values of mass spectra to integral values
- Several mass spectral databases used for the identification of metabolites in GC/MS measurements (EI) contain mass spectra in nominal m/z notation whereas MS instruments are able to obtain higher resolution.
- The mass spectral lookup using e.g. the dot-product of the query and database spectra is inapropriate if high resolution spectra are compared to spectra with nominal m/z entries. One possibility is to transform the high resolution spectra to integral m/z values. Alternatively, adapted scoring methods can be applied.
- High resolution mass spectra can be compared to nominal m/z spectra by rounding the measured m/z values to integral values.
- It is questionable if rounding at 0.5 is the best option.
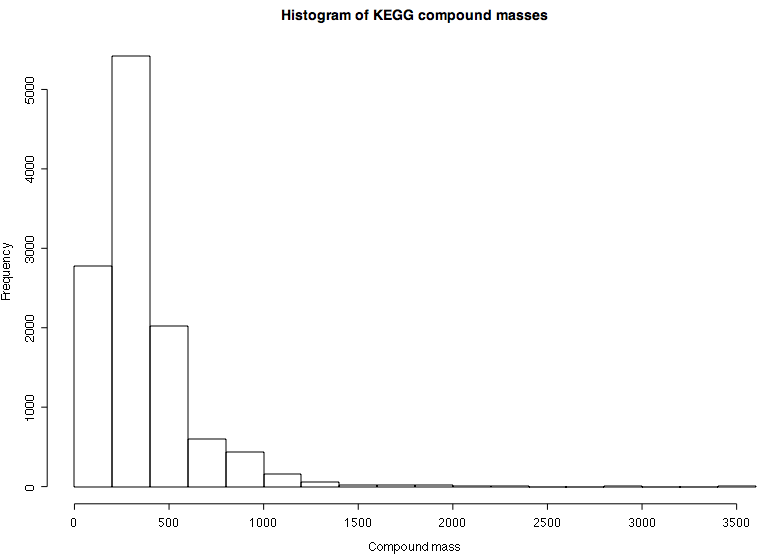
- The KEGG compounds database contains more than 10000 compounds with annotated masses and most of the masses are below 1000 Dalton.
- C, H, N, O, P, S are the main atoms of biologically relevant compounds.
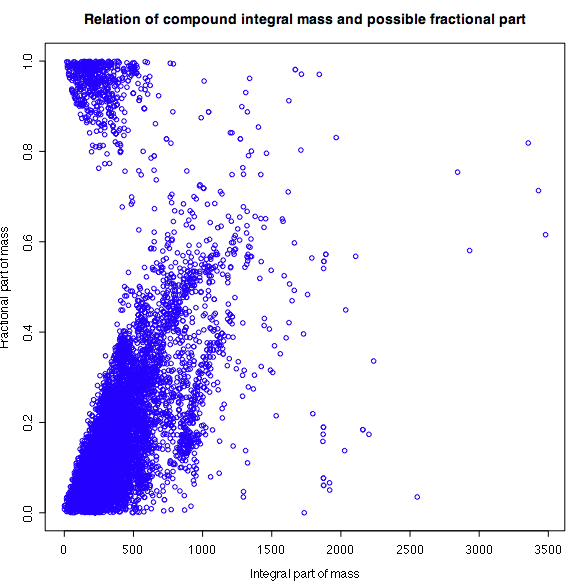
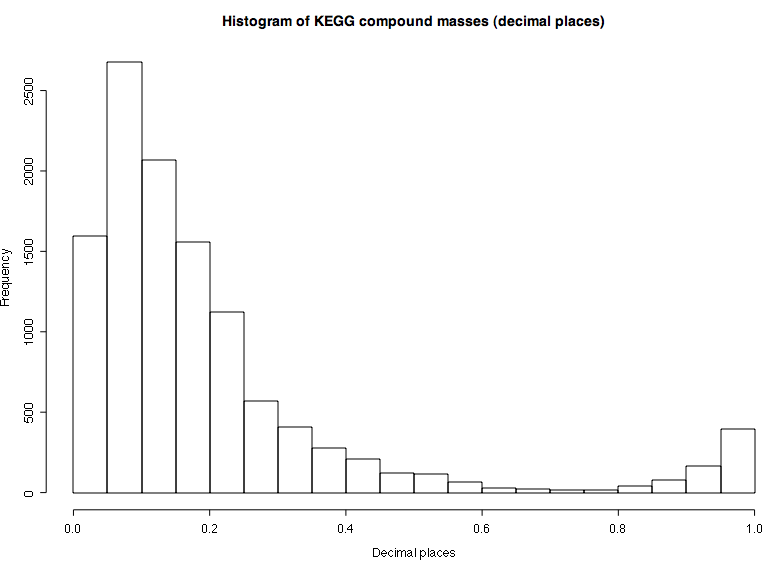
- The possible fractional values of the compound masses are dependent on the integral compound mass.
- In the fractional interval 0.7 to 0.75 only 15 compounds are listed in the KEGG compounds database.
- Mass spectrometric devices may drift, meassured m/z values can therefore vary.
- To round m/z to integral values as robust as possible, 0.7 instead of 0.5 may be used.
- For all m/z values detected by a MS instrument (EI, Ion Trap) for a complete chromatogram, the distribution of the values is comparable to that of the KEGG compounds.
- Again, in the fractional interval 0.7 to 0.75 only 0.3% of the m/z values are detected.
- This observation is also useful if extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) of GC/MS measurements with integral m/z values need to be generated without following individual m/z traces. Again, a rounding of the m/z values at 0.7 instead of 0.5 will provide more stable EICs.