GenDBWiki/DataModel: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "= The GenDB Data Model = Gen``DB is based on a data model with three core types of objects. ''Regions'' describe arbitrary (sub-) sequences. A region can be related to a parent ...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= The GenDB Data Model = | = The GenDB Data Model = | ||
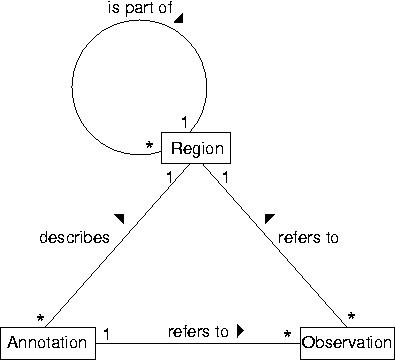
GenDB is based on a data model with three core types of objects. ''Regions'' describe arbitrary (sub-) sequences. A region can be related to a parent region, e.g. a CDS is part of a contig. ''Observations'' correspond to information computed by various tools (e.g. Blast or InterPro) for those regions. ''Annotations'' store the interpretation of a (human) annotator. They describe regions based on the evidence stored in the observations. | |||
[[File:GenDB-UML-DataModel.jpg]] | |||
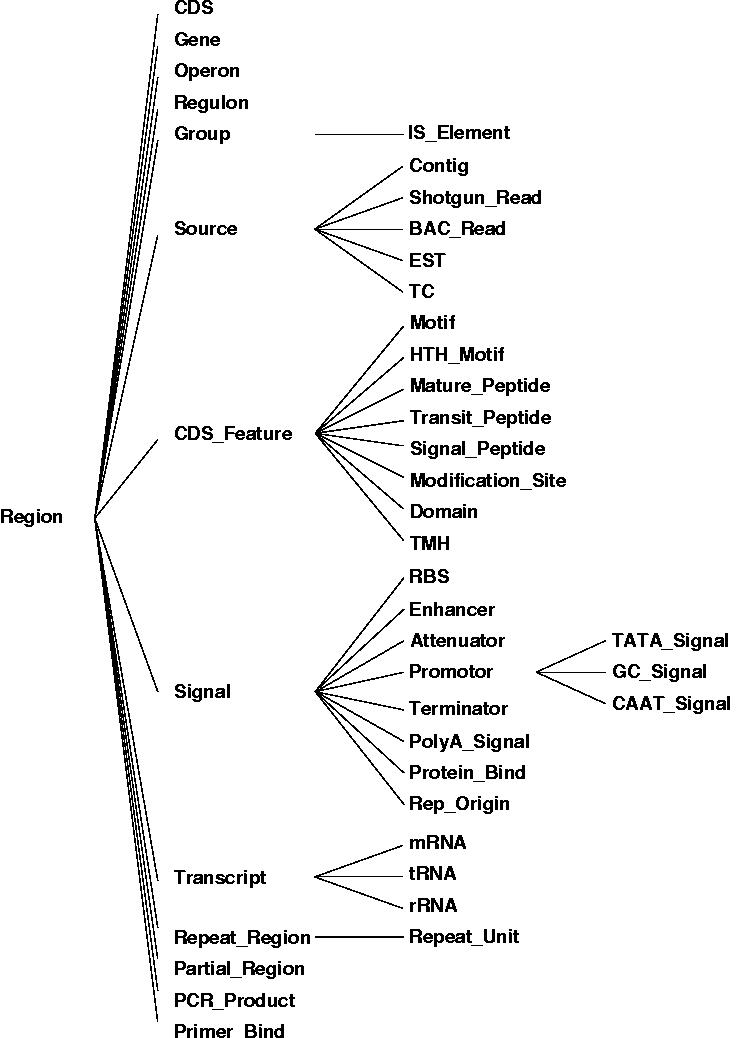
The figure shown above illustrates the relationships between the different core objects. As can be seen, there is a clear distinction between the results from various bioinformatics tools (observations) and their interpretation (annotations) which was implemented in the data model. While this data model seems very generic, it represents a hierarchy of classes, including the complete EM``BL feature set for prokaryotes with several extensions as illustrated in the figure below. | The figure shown above illustrates the relationships between the different core objects. As can be seen, there is a clear distinction between the results from various bioinformatics tools (observations) and their interpretation (annotations) which was implemented in the data model. While this data model seems very generic, it represents a hierarchy of classes, including the complete EM``BL feature set for prokaryotes with several extensions as illustrated in the figure below. | ||
[[File:GenDB-Regions.jpg]] | |||
to be continued ... | to be continued ... | ||
Latest revision as of 16:42, 31 October 2011
The GenDB Data Model
GenDB is based on a data model with three core types of objects. Regions describe arbitrary (sub-) sequences. A region can be related to a parent region, e.g. a CDS is part of a contig. Observations correspond to information computed by various tools (e.g. Blast or InterPro) for those regions. Annotations store the interpretation of a (human) annotator. They describe regions based on the evidence stored in the observations.
The figure shown above illustrates the relationships between the different core objects. As can be seen, there is a clear distinction between the results from various bioinformatics tools (observations) and their interpretation (annotations) which was implemented in the data model. While this data model seems very generic, it represents a hierarchy of classes, including the complete EM``BL feature set for prokaryotes with several extensions as illustrated in the figure below.
to be continued ...